STEM/STEAM
What is STEM/STEAM?
Explaining STEM/STEAM
Rather than teaching Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics as separate and discrete subjects, STEM integrates them into “interdependent” learning units based on real-world applications.
CORE EducationSTEAM is an educational approach to learning that uses Science, Technology, Engineering, the Arts and Mathematics as access points for guiding student inquiry, dialogue, and critical thinking.
– Susan Riley, Arts Integration Specialist
Education Closet
STEM/STEAM-based programmes take an integrated approach to learning and teaching, which requires an intentional connection between curriculum learning objectives, standards, assessments, and lesson design/implementation.
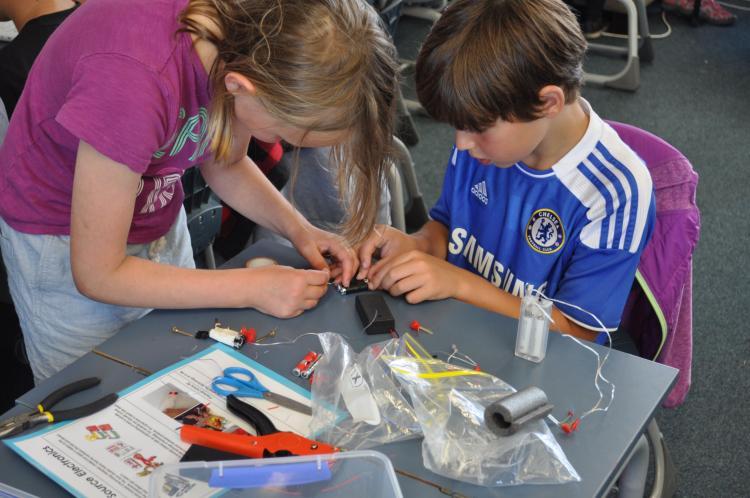
STEM/STEAM learning applies meaningful maths, science, and technology content to solve real-world problems through hands-on learning activities and creative design.
"STEAM is more than just the traditional science technology engineering arts and maths subjects on their own they're opportunities where subjects combine to form interesting new subjects such as bio engineering and biotechnology," explains John Durant, MIT Adjunct professor.
Adding the "A" to the STEM subject areas
The arts are a natural part of STEAM work. Products and structures are built according to creative designs. Scientific developments are explained through well-crafted communications.
Educators can design more wholistic STEM programs by integrating the arts.
“Integrating arts activities can decidedly enliven the curriculum content, make lesson outcomes more successful and interesting to both teachers and students, and introduce powerful and inspired creative thinking into the teaching-learning process.”
– Sousa and Pilecki, From STEM to STEAM: Using Brain-Compatible Strategies to Integrate the Arts, 2013
Why is STEAM important?
Global skill shortages in STEAM-related fields are redefining educational priorities. Schools are starting STEAM-based learning programmes to equip students with the skills and knowledge needed to thrive in the 21st century. STEAM learning will not only produce tomorrow's designers and engineers; it will develop innovative mindsets and the ability to problem-solve, ensuring that our students become creators of technology, not just passive consumers.
More information »
- Full STEAM ahead for 21st century citizens – Patrick Whittle interviews education experts on why STEAM is important for 21st century learning in New Zealand.
Benefits of STEAM learning
Students who participate in STEAM learning:
- think outside the box
- feel safe to express innovative and creative ideas
- feel comfortable doing hands-on learning
- take ownership over their learning
- work collaboratively with others
- understand the ways that science, maths, the arts, and technology work together
- become increasingly curious about the world around them and feel empowered to change it for the better.
More information »
- Developing STEAM Education to Improve Students’ Innovative Ability – An interview with STEAM expert professor Georgette Yakman goes deeper into how STEAM can develop students' innovative problem-solving abilities.
What does STEAM learning look like?
STEAM learning is inquiry
In an authentic STEAM lesson, the path to knowledge is anything but smooth. Questions are driven by the learners, and failure is reframed as part of the learning process. Goals, decisions, and solutions are generated by the students within the limitations of their learning context (such as access to materials and tools, or achieving curriculum standards). They control their own investigations. As long as the inquiry results in a product that provides a solution to a real problem, the inquiry is authentically STEAM.
4 different kinds of inquiry for STEAM-based learning
This post on steampoweredfamily.com talks about how different kinds of inquiry strategies can support STEM and STEAM learning.
STEAM lessons are authentic and focus on real-world problems
Careers in STEAM-related fields are all about solving real-world problems. Why should STEAM classrooms be any different? If students can address real problems in their social and environmental context, they will be able to make the connections between STEAM knowledge and their impacts on everyday life.
- Encourage students to identify problems themselves. Guide them to solve problems that relate to their environmental and social context.
- Guide student projects by using a framework for STEAM design. Use design thinking or engineering design process .
- Keep projects doable. Encourage students to aim high while doing projects that are realistically achievable within the limitations of their learning context.
- Start close to home by finding a problem on the school campus or in the neighbourhood.
More information »
STEM problems students can really address
Blog post by Anne Jolly gives tips and resources for helping your students drive problem-solving with STEM
STEM and STEAM learning can support the New Zealand curriculum
"Future focus is about supporting learners to recognise that they have a stake in the future, and a role and responsibility as citizens to take action to help shape that future."
By it's very nature, STEAM learning is future-focused. It empowers learners to change the world for the better by drawing on the connections between science, art, maths, engineering, and technology. STEAM-based projects can be an effective way to achieve curriculum objectives authentically.
STEM/STEAM in New Zealand schools
Chantelle’s journey with STEAM and UDL
Chantelle Rich, a year 5/6 teacher from Henderson North Primary, tells the NZC online blog how STEAM and UDL has transformed her practice.
Preparing for lift-off with real-world skills
This article from the Education Gazette talks about how Rototuna School integrated maths, science, and geometry to build rockets.
Te Papa: Hīnātore learning lab
Take a look at the innovative STEAM learning happening in Te Papa's education lab.
STEAM lessons apply maths and science
Authentic STEAM lessons are purposefully designed to integrate maths and science learning content. Measuring, calculating, testing, gathering and analysing data – when students are applying these skills to solving a problem, they can see the maths and science in what they are doing.
- Collaborate with other math, science, and art teachers to gain insight into how curriculum objectives can be incorporated into a STEAM lesson.
- Create powerful inter-disciplinary projects by sharing expertise and resources.
- Use maths authentically by collecting and analysing testing data, graphing, and taking measurements.
- Support STEAM learning by cementing students' understanding of key concepts through traditional-style quizzes.
Snapshots of learning
Gamifying STEAM
Gamified learning sparks engagement revolution
Leaders at St Thomas of Canterbury College lift engagement by embedding gamification and agency into learning. They apply maths and science using gameful approaches.
STEAM at Taita College
Cultural intelligence inspires authentic STEAM learning Taita College
Taking the rich cultural diversity of their student cohort as a starting point for deep learning, school leaders have been integrating NCEA units around authentic cultural contexts, such as the cooking of food in a hāngī and umu (Māori and Pacific earth ovens).
Web resources for integrating maths and science into STEAM lessons
The Steam Art Room: Making connections to science, technology, engineering, and math through art
Contains well-considered STEAM lesson plans.
Hacking STEM Lessons & Hands-On Activities
Integrated STEM lessons from Microsoft.
STEAM learning builds tuakana-teina relationships
Most real-world STEAM projects can only be achieved through the collaborative efforts of many individuals. In the STEAM classroom, collaborative projects are a chance for students to share ideas, get feedback from their peers, and develop soft skills.
- Model positive collaborative behaviour.
- Introduce digital tools and applications for collaborating.
- Establish teamwork procedures and rationale.
- Assess teamwork progress.
- Encourage students to share team successes with the rest of the class.
More information »
Co-Measure: developing an assessment for student collaboration in STEAM activities
This article from the International Journal of Stem Education reports on the development of a rubric for assessing student collaboration on STEAM-based projects.
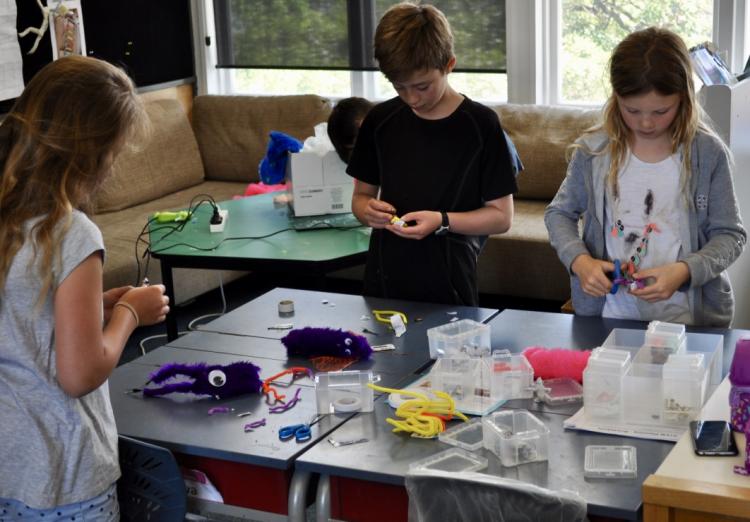
STEAM learning is hands-on and artistic
As students tackle challenges, create prototypes, test and re-test their designs, you can expect a fair amount of noise in the STEAM classroom. STEAM challenges require students to make, tinker and build. Bringing in methods from art and design can take STEAM projects to their full creative potential.
Use art to make STEAM learning more hands on:
- Design technologies and protypes for 3D printing in Tinkercad .
- Do graphic design around your prototype.
- Design apps for solving problems.
- Draw up design plans to reinforce your team's project vision.
- Do projects that explore connections between art, science and maths.
- Create appealing data visualisation using Piktochart .
- Document learning using digital media (video, photography, blog-writing, eBooks).
- Explain concepts from STEM using artistic solutions like programming a game in Scratch .
More information »
Kennedy Center
Website containing lessons that put the "A" in STEAM.
Education Closet
Contains resources and lesson plans that aim to integrate the arts into STEM.
More thinking around what makes up STEAM learning:
Anne Jolly: The eight criteria for STEM programs
Anne Jolly is a STEM expert from Alabama, America.
Essential components of a STEAM lesson
Ben Newsome is a proponent of STEAM education from NSW, Australia.
STEAM learning approaches
Some learning approaches widely used as frameworks for guiding students through STEAM learning
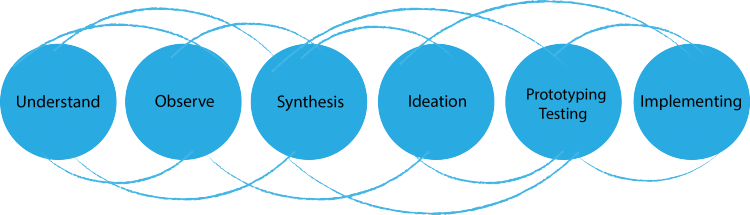
Design thinking
Design Thinking is a design methodology that provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It contains several different phases, including empathising, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing.
Engineering design process
The Engineering Design Process (EDP) is a step-by-step method of solving a problem by creating something tangible with a specific function.
Project-based learning
STEAM learning fits in really nicely with the goals and aims of project-based learning. Perhaps the only difference is that STEAM has an engineering focus.
Computational thinking
Computational thinking enables a student to express problems, and formulate solutions in a way that means a computer (an information processing agent) can be used to solve them.
Makerspaces
A more relaxed and open-ended version of STEAM, Makerspaces are places where students can follow any kind of interest that involves making, creating, tinkering, programming, and designing.
Getting started with STEAM learning
Decide on a vision for your STEAM program
STEAM is more than building robotics. It is also more than coding, or doing a science experiment. STEAM is applied knowledge. It is using principles from multiple learning areas to solve real-world problems. To develop an authentic STEAM program, think deeply about how you can integrate maths, science, art, and technology into hands-on learning activities.
Industry, business, and community partnerships
STEAM programs can be greatly strengthened by organising some school partnerships. Universities, hospitals, and local businesses are often willing to donate usable equipment they are replacing, as well as share expertise. A visit to STEAM-related businesses and organisations could provide your students with industry insights, as well as possible contacts for help with projects. Connections made could even lead to careers post-school. These same businesses may also become alert to what you are trying to achieve in your classroom and may want to assist or provide resources.
School-industry partnerships strengthen STEM programs
This article describes how an Australian school teamed up with a local nursery to improve their agricultural STEM projects.
Get comfortable with the maths and science
Try to make sure there is a maths and science component to each STEAM project. If you mainly teach art, then talk to the maths teacher about finding a relevant maths connection, and vice versa.
Assessment
Think ahead of time about criteria for success. When deciding how to evaluate "success," remember that failure is an accepted part of STEAM learning.
Claire Amos talks about how to approach the Digital Technologies Curriculum, and the many benefits of STEAM education in New Zealand schools.
Assessment for STEAM learning
There are many aspects of STEAM learning that you may want to assess, including learning content knowledge, soft skills, or the design process. Ensure that your assessment is formative and summative; give your students goals to work towards while providing feedback on their progress.
You could assess, for example:
- student persistence
- improvement progress
- meeting of curriculum achievement objectives
- collaboration and teamwork
- content knowledge
- content application
- design success.
Allow flexibility in your rubrics to account for multiple learning paths and project variation.
Pacific STEAM
Use the resource to encourage students to study STEAM subjects and carry their ancestors' legacy into the future. Five short videos and downloadable posters illustrating how Pacific peoples were always scientists, technologists, engineers, artists, and mathematicians.
Planning and professional development
STEAM is an integrated approach to learning which requires an intentional connection between curriculum objectives, assessments, and lesson design/implementation. To develop a successful programme, schools must consider a variety of factors, including:
- collaborative planning, including a cross-section of teachers on each team
- adjusting timetables to accommodate a new way of teaching and learning
- professional development for all staff in STEAM practices and principles
- STEAM mapping for the curriculum and assessment design process
- alignment and unpacking of standards and assessments
- seamless lesson implementation processes and strategies.
Chantelle Rich shares her experiences with STEAM education. Chantelle offers tips and advice for others starting their journey, particularly around budgets, and how to bring the A into STEAM learning.
Getting help with STEM and STEAM in New Zealand
Professional development and resources available to schools embarking on STEM/STEAM journeys
STEM online NZ
Digital resources from the University of Auckland, designed to help teachers establish STEM programmes.
WEN Outreach visits
Women in Engineering (WEN) visits inform female-identifying people in high schools across New Zealand about engineering. Students partake in activities related to the physics and calculus NCEA curriculum or non-technical problem-solving for younger students. The Outreach volunteers, studying engineering themselves, lead the sessions.
OMGTech!
Develops & delivers engaging workshops for both teachers and students on digital technologies and how to explore and invent with them.
New Zealand science teacher
Contains courses and resources related to STEM.
Modern teaching aids STEM and makerspace kits
Contains introductory STEM kits with materials, tools, and resources.
Designing your own STEAM lessons
Use the following STEAM templates to guide your own decisions when planning lessons:
STEAM lesson plan template
From steamedu.com.
Plan Engaging STEAM Lessons: STEAM Lesson Plan Template
Engaging STEAM lesson template from Math Geek Mama.
STEM lesson specifications
Is your lesson authentically STEM? Use this STEM lesson design tool by Anne Jolly to create authentic STEM lessons.
Find STEAM lessons online
Do a google search for "STEAM lesson plans," and you'll find hundreds of resources. Not everything you find online will fulfil all the aspects of an authentic STEAM lesson. Try to ensure that the lessons you find address all or most of the following components of a STEAM lesson:
- The lesson contextualises maths, science, and art.
- The lesson is collaborative.
- The lesson results in a technology that solves a real-world problem.
- The lesson allows for multiple solutions (there isn't one right answer to arrive at).
- The lesson is hands-on and artistic.
More information »
How to analyse a lesson for STEM potential
This blog post from Anne Jolly lists criteria for finding STEM lessons that will genuinely challenge your students to problem-solve and create.
STEAM lesson plans
The Steam Art Room: Making connections to science, technology, engineering, and math through art
Contains well-considered STEAM lesson plans.
Hacking STEM Lessons & Hands-On Activities
Integrated STEM lessons from Microsoft.
PBS Learning Media: Engineering and Technology Lessons
Steam lessons with a hands-on, engineering focus.
- Do your own search to find even more.
Digital tools for STEAM
Gamefroot
Teaches students how to code games using a fun learning platform. It makes connections to the New Zealand curriculum.
The PocketLab
Pocketlab is an easy-to-use data collection tool aimed at aiding STEAM education. It can integrate with your device to provide sensory data on a range of physical and environmental forces, from motion to temperature.
Scratch
A learn coding tool for designing games and animations.
Learning resources to teach 3D modeling, whether you're starting a new design program, preparing students for certification, or looking to augment your curriculum.
Algodoo
An intuitive and appealing physics builder and simulator. Play around with different parameters like gravity, friction, restitution, refraction, attraction, etc and analyse them using their data visualisation tools.
Codecademy
Coding lessons helping learners design apps and websites from scratch.
Minecraft: Education edition
Create, design, and build with Minecraft.
SketchUp
Intuitive 3D design tool. Excellent tool for designing STEAM project plans and prototypes. SketchUp Pro is funded for New Zealand schools to use by the Ministry of Education.
Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a simple, student-friendly online 3D design and 3D printing app.
Sorry, no items found.
Readings
Closing the STEM gap: Why STEM classes and careers still lack girls and what we can do about it
This American research indicates conditions and context can make a significant difference to encouraging girls into STEM subjects. Showing them how STEM is applicable outside the classroom influences choices.
Full STEAM ahead for 21st century citizens
Patrick Whittle interviews education experts on why STEAM is important for 21st century learning in New Zealand.
Anne Jolly: The eight criteria for STEM programs
Anne Jolly is a STEM expert from Alabama, America.
Essential components of a STEAM lesson
Ben Newsome is a proponent of STEAM education from NSW, Australia.
Co-Measure: developing an assessment for student collaboration in STEAM activities
This article from the International Journal of Stem Education reports on the development of a rubric for assessing student collaboration on STEAM-based projects.
STEM problems students can really address
Blog post by Anne Jolly gives tips and resources for helping your students drive problem-solving with STEM.
4 different kinds of inquiry for STEAM-based learning
This post on steampoweredfamily.com talks about how different kinds of inquiry strategies can support STEM and STEAM learning.
School-industry partnerships strengthen STEM programs
This article describes how an Australian school teamed up with a local nursery to improve their agricultural STEM projects.
STEM/STEAM in New Zealand schools
Chantelle’s journey with STEAM and UDL
Chantelle Rich, a year 5/6 teacher from Henderson North Primary, tells the NZC online blog how STEAM and UDL has transformed her practice.
Full STEAM ahead at Kadimah School
This article describes how Kadimah school integrated STEAM with the NZC.
Preparing for lift-off with real-world skills
This article from the Education Gazette illustrates how Rototuna School integrated maths, science, and geometry to build rockets.
Te Papa: Hīnātore learning lab
Take a look at the innovative STEAM learning happening in Te Papa's education lab.
STEAM web resources
The Steam Art Room: Making connections to science, technology, engineering, and math through art
Contains well-considered STEAM lesson plans.
Hacking STEM Lessons & Hands-On Activities
Integrated STEM lessons from Microsoft.
Education Closet
Contains resources and lesson plans that aim to integrate the arts into STEM.
Careers with STEM magazines
The Issuu website contains a range of careers magazines across science, technology, engineering and maths that you can view online and share with students.
STEAM-based learning approaches
Design thinking
Design Thinking is a design methodology that provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It contains several different phases, including empathising, defining, ideating, prototyping, and testing.
Engineering design process
The Engineering Design Process (EDP) is a step-by-step method of solving a problem by creating something tangible with a specific function.
Project-based learning
STEAM learning fits in really nicely with the goals and aims of project-based learning. Perhaps the only difference is that STEAM has an engineering focus.
Computational thinking
Computational thinking enables a student to express problems, and formulate solutions in a way that means a computer (an information processing agent) can be used to solve them.
Makerspaces
A more relaxed and open-ended version of STEAM, Makerspaces are places where students can follow any kind of interest that involves making, creating, tinkering, programming, and designing.
App development in the classroom
Practical information and resources to support teaching app development in your classroom.
Tools for designing your own STEAM lessons
STEAM lesson plan template
From steamedu.com.
Plan Engaging STEAM Lessons: STEAM Lesson Plan Template
Engaging STEAM lesson template from Math Geek Mama.
STEM lesson specifications
Is your lesson authentically STEM? Use this STEM lesson design tool by Anne Jolly to create authentic STEM lessons.
STEM by design
Anne Jolly's hub for STEM learning has loads of practical tips and examples for designing STEM lessons.
Help with STEAM and STEM in New Zealand
STEM online NZ
Digital resources from the University of Auckland, designed to help teachers establish STEM programmes.
OMGTech!
Develops & delivers engaging workshops for both teachers and students on digital technologies and how to explore and invent with them.
New Zealand science teacher
Contains courses and resources related to STEM.
Modern teaching aids STEM/STEAM kits
Contains introductory STEAM kits with materials, tools, and resources.
Digital tools for STEAM
Gamefroot
Teaches students how to code games using a fun learning platform. It makes connections to the New Zealand curriculum.
The PocketLab
Pocketlab is an easy-to-use data collection tool aimed at aiding STEAM education. It can integrate with your device to provide sensory data on a range of physical and environmental forces, from motion to temperature.
Scratch
A learn coding tool for designing games and animations.
Autodesk STEAM
Projects using knowledge of STEAM, design thinking, and collaboration to create innovative solutions to design problems.
Algodoo
An intuitive and appealing physics builder and simulator. Play around with different parameters like gravity, friction, restitution, refraction, attraction, etc and analyse them using their data visualisation tools.
Codecademy
Coding lessons helping learners design apps and websites from scratch.
Minecraft: Education edition
Create, design, and build with Minecraft.
SketchUp
Intuitive 3D design tool. Excellent tool for designing STEAM project plans and prototypes. SketchUp Pro is funded for New Zealand schools to use by the Ministry of Education.
Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a simple, student-friendly online 3D design and 3D printing app.